Lymphedema: What You Need to Know
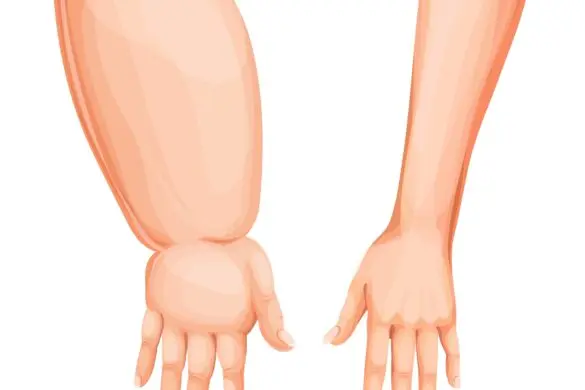
Lymphedema is a condition characterized by swelling, usually in the arms or legs, that can occur after cancer treatment—especially when lymph nodes are removed or damaged during surgery or radiation therapy.
when the lymphatic system, is blocked or impaired. While it cannot always be prevented, early detection and proper care can significantly reduce its impact.
It most commonly affects people who have had surgery or radiation for breast, melanoma, gynecologic, or prostate cancers.
Common Symptoms
Swelling in the arm, hand, leg, or foot
A feeling of heaviness or tightness
Restricted range of motion
Pain or discomfort
Recurring infections (e.g., cellulitis)
Hardening or thickening of the skin
How Can You Manage Lymphedema?
1. Exercise
Gentle, controlled exercises can help move lymph fluid out of the affected limb. Examples include light stretching, walking, swimming, or yoga. Always consult your doctor or a physical therapist before starting any routine.
2. Skin and Wound Care
Maintaining healthy skin is crucial to prevent infections:
Keep skin clean and moisturized
Avoid cuts, burns, or insect bites
Use gloves when gardening or doing household chores
Look out for any signs of cellulitis and inform your doctor at the earliest
3. Diet Changes
Lymphedema can worsen with weight gain. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition helps reduce swelling. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and reduced sodium intake.
4. Regular Medical Check-Ups
Your medical team may detect early changes before you notice them. Attend all follow-up appointments and report any new swelling or discomfort promptly.
Can Lymphedema Be Prevented?
While not always preventable, risk can be minimized by avoiding injury to the affected limb, not having blood draws or blood pressure measurements on that side, and wearing compression garments when advised.
With proper self-care and medical support, many people successfully manage lymphedema and maintain an active, healthy lifestyle.
